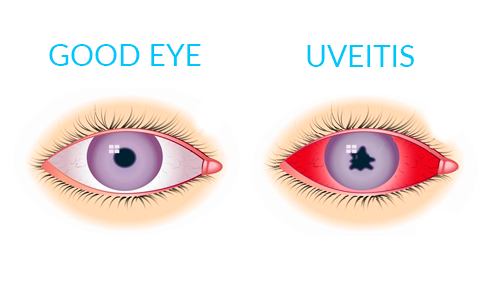
 Uveitis is a form of eye inflammation. It affects the middle layer of tissue in the eye wall (uvea). Uveitis (u-vee-I-tis) warning signs often come on suddenly and get worse quickly. They include eye redness, pain and blurred vision. The condition can affect one or both eyes.
Uveitis is a form of eye inflammation. It affects the middle layer of tissue in the eye wall (uvea). Uveitis (u-vee-I-tis) warning signs often come on suddenly and get worse quickly. They include eye redness, pain and blurred vision. The condition can affect one or both eyes.
Possible causes of uveitis are infection, injury, or an autoimmune or inflammatory disease. Many times a cause can’t be identified. Uveitis can be serious, leading to permanent vision loss. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent the complications of uveitis.
Patients with uveitis are also at increased risk of developing glaucoma because of the uveitis itself, and because of the use of corticosteroids which are the mainstay of uveitis treatment.
Image description: Left side shows an eye that is not affected by inflammation. Right side shows the same eye, with the shape of the pupil no longer circular, and the sclera (the white area) red and inflamed.